Thousands of Brits could be misdiagnosed with the silent killer after a screening test
THOUSANDS of Brits are at risk of being mistakenly diagnosed with diabetes after a faulty blood test at an NHS Trust.
Bedfordshire Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust has revealed it has experienced a “temporary problem” with its HbA1c blood test and diabetes monitor.

1
The trust admitted that it may have caused a mix-up of blood samples at Luton and Dunstable University Hospital “where it is possible that some patients received HbA1c results that could have been higher than they actually were”.
It is understood that up to 11,000 patients in south Bedfordshire are at risk of being affected – and the trust has confirmed it is now in the process of contacting them.
A spokesman said: “In the coming weeks you may receive a call from the hospital asking you to take another blood sample so that you can be tested again.”
“Please be assured that we will contact you if your result is affected. We ask residents to avoid calling the hospital or themselves. GP asking if they need to be re-examined because we need to focus our energy on scheduling re-examinations with patients who need them.
“Please do not go for the HbA1c test again if you have not contacted the hospital directly by phone or letter.
“If you have received the letter, please make sure you have the blood request form that was given to you. If you go and do not need the test, you will be turned away.”
The trust also apologized to patients for the mix-up: “We sincerely apologize for the distress and inconvenience this has caused.”
“We do a complete job examination to find out what went wrong and learn any lessons.”
Type 2 diabetes causes high blood sugar levels that can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
This condition can go undiagnosed for years because its symptoms are hard to see or are dismissed as something else.
In February, the main lesson in Office of National Statistics (ONS) has revealed that more than a million Brits have type 2 diabetes – and don’t know it.
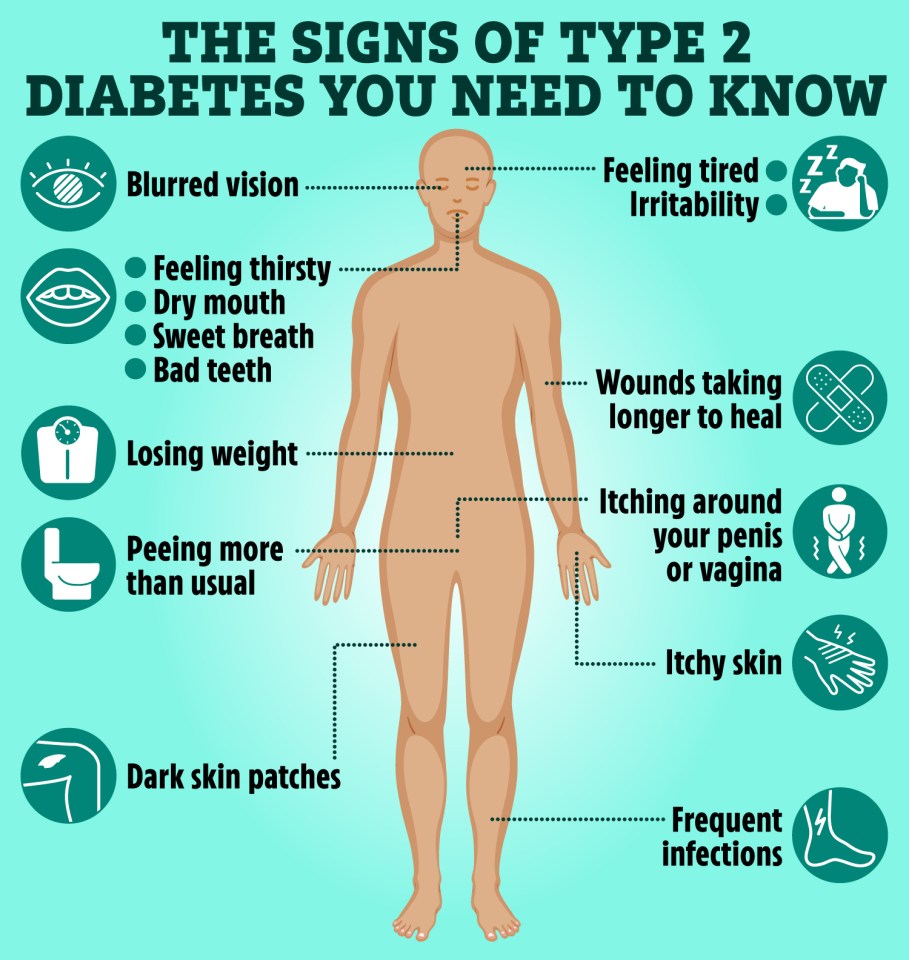
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
According to the NHS, symptoms of type 2 diabetes to look out for include:
- Urinating more often, especially at night
- Feeling thirsty all the time
- Feeling very tired
- Losing weight without trying
- Itching around your penis or vagina, or having frequent thrush
- Getting cuts or bruises takes a long time to heal
- Having blurred vision
These are the most common symptoms that are often reported by people with this disease.
You should visit your doctor if you have any of these symptoms.
However, there are many other unusual symptoms that may alert you to this disease.
These include:
- Dark skin
- Frequent infections
- Itchy skin
- Dry mouth
- Irritation
- Sweet soul
- Tingling or numbness
- Bad teeth
What are the risk factors for type 2 diabetes?
By Isabel Shaw, Health Correspondent
You are at risk of developing type 2 diabetes if you are over 40, or 25 for South Asians.
Having a close relative with type 2 diabetes, such as a parent, brother or sister, also puts you at greater risk – as does being overweight or obese.
Those who are South Asian, Chinese, African Caribbean or black people from Africa – even if you were born in the UK – are also at high risk.
You can take an online test to find out your risk of this disease.
A quick question asks about age, weight, if anyone in the family has diabetes and if you’ve been told you have high blood pressure, for example.
It will give a score between zero and 47 points.
The higher the risk level, the more likely a person will develop type 2 diabetes in the next 10 years.
For example, one in four people at high risk will develop type 2 diabetes in the next 10 years.
If a person’s score is limited or high, they can self-refer to local services for remote or online support without going to a health professional.
It does not necessarily mean that a person has prediabetes – when blood sugar is higher than normal but not high enough to be considered type 2 diabetes.
How do I treat type 2 diabetes?
If you are diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, you will need to eat a healthy diet, exercise regularly and have regular check-ups, including blood tests.
Try to quit smoking if you smoke, and limit your alcohol intake.
Type 2 diabetes can get worse over time, and people living with type 2 diabetes often need medication, usually tablets or injections.
However, some people can reduce type 2 diabetes by losing weight, where blood sugar is reduced below the diabetic threshold.
Some people can do this with a low-calorie diet, but this is not suitable for everyone, so it is important to get medical advice first.
What is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
IF you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes, it means that there is too much sugar (a type of sugar) in your blood due to a problem with the hormone insulin.
Both are serious conditions that can cause serious health problems.
However, there are differences between the causes, onset of symptoms and treatment of type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes.
TYPE 1
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition and accounts for five to ten percent of all people diagnosed with diabetes.
The immune system attacks the pancreas and destroys the cells that produce insulin.
TYPE 2
Type 2 diabetes is 90-95 percent of all patients with diabetes.
With this type of disease, the body’s cells become resistant to insulin, so more insulin is needed to keep blood sugar within a normal range.
Type 2 is usually caused by certain lifestyle factors, such as being overweight.
#Thousands #Brits #misdiagnosed #silent #killer #screening #test
